Storage systems classification
Considering any information system, one cannot but highlight such a process as information storage. It is the information that is the main value in any organization, and the entire infrastructure designed for its processing, storage, transmission & ndash; only a consequence of this fact. I would like to pay attention to the process of storing information, methods of hardware protection of information from loss and management of information storage. In the modern world, any company experiences the following trends: information plays a key role in the work of an organization, data growth occurs in an exponential proportion. For example, IDC claims that the volume of information generated and duplicated annually will increase 6-fold between 2006 and 2010.
First of all, I am interested in long-term storage on hard disks (in the future, on SSD drives). This material gives an idea of the hardware methods of organizing data storage and protection. The hierarchy of data storage systems on hard disks and their general classes are considered. Systems such as NAS servers or VTL were not considered, although they may take place as an add-on to the systems described.
Threats to information, leading to its loss when stored on hard drives
- Hardware - failure, damage, equipment breakdown.
- Software - failure, failure, incorrect operation of the software.
- Human - wrong, inappropriate actions of the personnel.
- Infrastructural - failure of media, broken cables, turning off routers, bad contacts.
- Power supply - data loss due to poor quality or power outage.
- Accidents - fire, flooding and other threats on the scale of a server room, building.
- Disasters are problems of a district, city scale.
So, starting from simple to complex.
Direct HDD connection
The hard drive is connected to the motherboard integrated controller. It is understood that there are no additional storage devices. If this type of connection is almost always implemented at home, then for any company it is completely unacceptable as a means of storing at least some important information.

Data is not protected and any failure (hardware or software) can and will one day lead to data loss. The value of your information is opposed not only to the manufacturer's forecasts for warranty costs, but also to the quality of electricity, personnel qualifications, software and other supra-system factors.
Information is not protected from:
- Hardware Problems
- Software glitches
- Human Factors
- Infrastructure Issues
- Power outages
- Alarms
- Disasters
Internal RAID Controller
RAID (redundant array of independent/inexpensive disks) - a redundant array of independent/inexpensive hard disks & mdash; a matrix of several disks controlled by the controller, interconnected by high-speed channels and perceived as a single whole. Depending on the type of array used, it can provide varying degrees of fault tolerance and performance.
Two or more disks are connected to the controller in the server, or an external disk enclosure is connected to the controller, depending on the selected level of fault tolerance, protects one or more disks from failure, while maintaining operability.
With nonvolatile cache and SAS disks, protects against power outage problems unless electrical damage occurs to the equipment. But if the server is damaged, data loss is possible.
Protects data from:
- Hardware problems - failure, damage, equipment breakdown. Partially, only from the failure of hard drives.
- Power failures - partially protects data stored in the controller buffer in the write queue, but for a limited time and only if there is a battery on the controller.
Doesn't protect against:
- Software crashes
- Human Factors
- Infrastructure problems (although all connections are usually inside the server).
- Alarms
- Disasters
The main purpose of the application is to protect data from loss in case of hard disk failure, also, one of the reasons for implementation is the need for increased performance of the disk subsystem.
RAID controllers are supplied by many companies: IBM, DELL, SUN, HP, Adaptec, 3ware, LSI, and others.
External RAID array
Initial level. Disks and controller are placed in a separate external system. One or more servers can be connected to an external array with different interfaces, for example SAS, iSCSI, FC. Almost all such systems have redundant fans and power supplies, many provide for the possibility of installing a redundant controller. By themselves, external RAID arrays are more efficient and reliable than internal RAID controllers and can expand to over a hundred drives (using disk shelves).

At the moment, many models have advanced monitoring and management tools, both the array itself and the data on it. The means of monitoring the health of disks inform about a possible failure in advance, most worthy manufacturers change disks only on the basis of these messages, until the fact of inoperability. Some models have the ability to take snapshots - (snapshot), which protects data and simplifies backups.
Protects data from:
- Hardware problems - partially, with duplication of all systems.
- Software glitches - in part, some arrays have snapshot functionality that will help create multiple snapshots.
- Infrastructure Issues - Protect by duplicating all arrays outside the server.
- Power failures - partially protects data in the controller buffer for writing when a battery is present. The presence of redundant power supplies ensures greater reliability.
Doesn't protect against:
- Human Factors
- Alarms
- Disasters
The reason for implementation is either the need to consolidate storage resources, their easier management, the possibility of simultaneous access (for example, when creating a cluster), or the need for high performance, or the need for greater reliability (duplication of paths to the controller) .
Typical representatives of the class: Xyratex 5xxx/6xxx, Dell MD3000, IBM 3XXX, HP MSA 2000.
Enterprise disk array
Medium level. Sometimes it is quite difficult to draw the line between Entry level and Midrange, but mainly the leading manufacturers agree that the main criterion is the reliability of the system and its functionality. Performance or scalability, which are naturally larger, also matters, but not in the foreground. Naturally, middle-level systems have everything that is in the entry level and even more - duplication of all systems, including controllers, interconnects, power supply, is considered mandatory, we can say that 99.99% availability for such systems is already at least (less than an hour downtime per year) and the new standard is 99.999. And, accordingly, a rich set of management and monitoring tools. A wide range of options is possible for each system, for example, synchronous and asynchronous replication, volume copying, a set of utilities for both the server and the array.
Thus, by means of replication it is possible to achieve from the system resistance to accidents and even catastrophe, by means of one array alone.
Protects data from:
- Hardware problems.
- Software glitches - partially, all arrays have snapshot functionality.
- Human Factors - in part, a more advanced management system, as a rule, tries to prevent wrong actions.
- Infrastructure Issues - Protect against duplication of all systems outside the array.
- Power failures - partially protects data in the controller's buffer for writing when there is a battery on the controller. The presence of redundant power supplies ensures greater reliability.
- Alarms - when replication systems are running.
- Catastrophes - when remote replication systems are running.
When applied. The reason for the transition to systems of this level can be either the need for additional services for redundancy, or reducing the cost of maintaining the infrastructure. The company may also be interested in a more rational distribution of resources (and hence savings), which is achieved due to the high scalability of such systems, the use of virtualization technologies. We must not forget about high standards of reliability.
Typical representatives of the series: HP EVA (pictured), DELL EqualLogic, IBM DS 4xxx
Hi-End storage systems
Hi-end system. These systems are in demand only by large corporations, which, given their cost, is quite understandable. Delivering near-absolute reliability and unique functionality. Not being able to reveal all the functionality within the framework of this material, we can unequivocally say that these solutions justify their cost, if, of course, you have several million dollars.
These systems are based on the so-called non-stop systems. All system components are duplicated, including processors, the operating system is tested to exclude any errors, so the probability of failure is extremely small. In addition, the software supplied with this system is of considerable value.

In fact, these devices are no longer a means of storing information, but a solution for data management and virtualization, representing a complex solution that goes beyond the organization of simple information storage.
This equipment is supplied by leading manufacturers HDS, HP, IBM, EMC, SUN. (in the picture Hitachi USP V).
A few words about RAID arrays
RAID (redundant array of independent/inexpensive disks) redundant array of independent/inexpensive hard disks - a matrix of several disks controlled by the controller, interconnected by high-speed channels and perceived as a single whole. Depending on the type of array used, it can provide different degrees of fault tolerance and performance. Serves to improve the reliability of data storage and/or to increase the speed of reading/writing information (RAID 0).
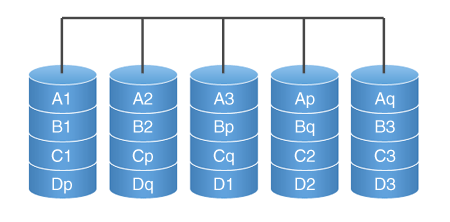
RAID 0
RAID 0 ('Striping') is a disk array of 2 or more disks in which information is split into A n blocks and written sequentially to hard disks. Accordingly, information is written and read simultaneously, which increases the speed.
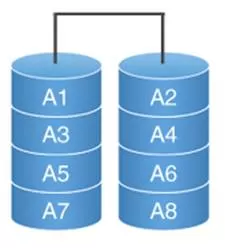
Unfortunately, if one of the disks fails, the information is irreversibly lost, so it is used either at home, or to store the paging file, swap file.
RAID 1
RAID 1 (Mirroring). In this case, one disk completely repeats the other, which guarantees performance in the event of a breakdown of one disk, but the amount of usable space is halved. Since discs are purchased at the same time, in the event of a defective batch, both discs may fail. The write speed is approximately equal to the speed of writing on one disk, it is possible to read from two disks at once (if the controller supports this function), which increases the speed.
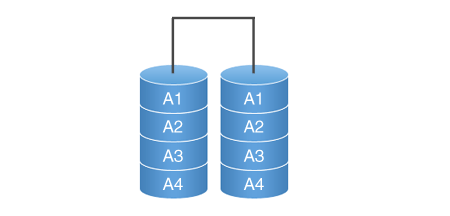
Most often used in small offices for databases, or for storing the operating system.
RAID 5
RAID 5. In this case, all data is divided into blocks and for each set the checksum is calculated, which is stored on one of the disks - it is cyclically written to all disks in the array (alternately on each one), and is used for recovery data. Resistant to no more than one disk loss.
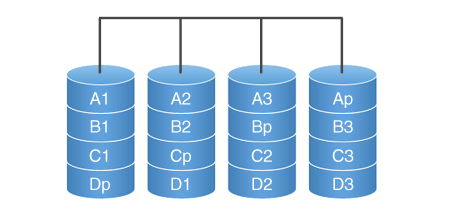
RAID 5 has high read rates - information is read from almost all disks, but reduced write performance - a checksum is required. But the most critical operation is rewriting, as it takes place in several stages:
- Reading data
- Read checksum
- Comparison of new and old data
- Writing new data
- Write new checksum
Used when a large volume is required, and a high reading speed.
RAID 6
RAID 6 (ADG). Logical continuation of RAID 5. The difference is that the checksum is calculated 2 times, and, as a result, it has greater reliability (resistant to failure of more than 2 disks) and lower performance.
RAID 10
RAID 10 (RAID 1 + 0). Combines the principles of RAID 0 and RAID 1. In its application, each hard disk has its own "mirrored pair", which uses half of the usable space. It is efficient as long as there is one working disk from each pair. Highest write/rewrite rates, comparable to RAID 5 in read speed. It is used for storing databases under high load.
Dmitry Nechaev
10/03.2009